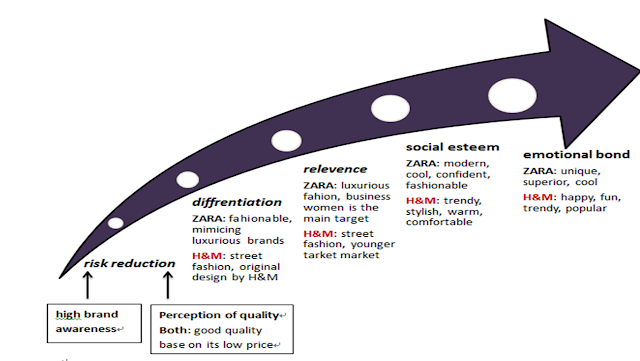
Although
ZARA and H&M are both in the fast fashion industry, the perception of ZARA
and H&M are different. To understand the differences between these two global
brands, we use BMS models to analyze.
Stage 1: awareness &
quality
H&M
and ZARA both dedicate in fast fashion industry, selling stylish clothing
worldwide. They both have high brand awareness, spreading fast and winning
great recognition. Considering their fashionable design and the low price, the
quality is good. Consumers can own those fashionable items and dress themselves
as super stars without spending much budget.
Stage 2:
A)
Differentiation
Although ZARA and H&M are both selling fast fashion
clothing, their positions are different. ZARA focuses more on the fashion items
like the luxurious brands, for example, LV and CHANEL. ZARA dispatches young
designers to participate in those fashion shows and sketch the latest design.
Then ZARA can produce those designs by itself with the fastest movement, even in
advance of the luxurious brands.
Regarding to H&M, its design style is more for street
fashion. Consumers can wear H&M’s clothing in everyday life. H&M also
hires designers to create original pieces, and sometimes invites famous
designers to collaborate together.
B)
personal
relevance & appropriate for consumer
ZARA’s black and white logo symbolizes its cool, individualistic
character. ZARA targets on 25-35 years old people, and it provides fashionable
clothing which is very suitable for business dressing or elegant party look.
Regarding to H&M, it focus more on young people and teenagers
instead. It focuses on 20-35 years old people, providing street fashion.
H&M is very close to consumers. It sells not only daily dressing like basic
sweaters but also the chic party look.
Stage 3:
A)
social esteem
By the images, websites, communication ways, ZARA creates a cool
and fashionable touches to consumers. The images of ZARA always are a person
wearing modern clothing standing in front of clean, pure color wall. Without
creating situation of wearing ZARA’s clothing, ZARA uses its modern,
fashionable products to attract the public. Wearing ZARA is equal to fashion.
In H&M’s communication way, consumers can see people in
trendy clothing having fun together. The people in the pictures can be a very
normal person like you and me, and that means H&M is suitable for everyone
in everyday occasion. Consumers feel comfortable and stylish when they wear
H&M.
B)
personal
emotional bonds
ZARA gives consumers an emotion that you are the one who is
keeping up with the latest fashion. You are unique and superior. However,
H&M releases the messages that you can be stylish and popular. With much more
atmosphere of happiness and fun, H&M is trendy also friendly. Both of them
seize the consumer needs that they want to be as fashionable as the celebrities
and want the latest trendy look with best price.